Guide to ERAS Telerobotics¶
| Author: | Siddhant Shrivastava |
|---|
Introduction¶
ERAS Telerobotics is a feature introduced in 2015 as part of the Google Summer of Code Program with the Italian Mars Society to support Telerobotics in Mars Missions. Telerobotics is a specialized field of space robotics that entails teleoperative control of Robots by Human beings vis-a-vis various channels -
- Joystick/Keyboard Control
- Gesture based shadowing of Astronauts
- Another Robot’s movements
ERAS Telerobotics uses all three of the above channels for the Husky Unmanned Ground Vehicle to test its Telerobotics platform. It is based on the Robot Operating System (ROS) for its high-performance, ease-of-use, distributed nature and open community.
This document is intended to be a walkthrough of the current state of ERAS Telerobotics.
On a high level, Telerobotics is supposed to look like this -
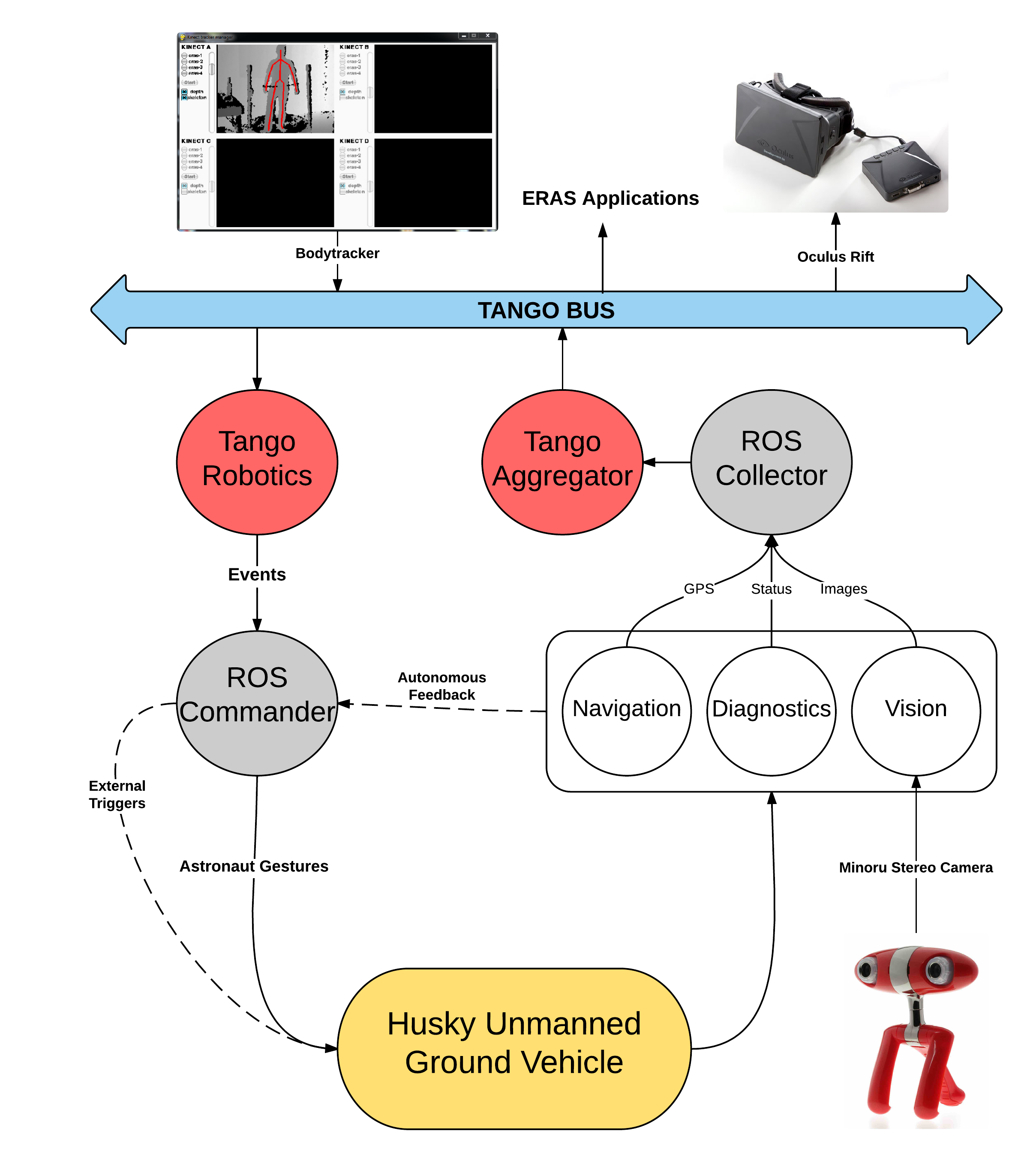
Setup of ERAS Telerobotics¶
The best way to get started is to use the existing Docker image
Understanding ERAS Telerobotics¶
Bulk of the Telerobotics platform makes use of the Python programming language. The three major libraries that this project is based on are -
- Robot Operating System
- Tango-Controls
- FFmpeg
Interfaces with other ERAS components¶
Telerobotics is a highly integrated application and seamlessly integrates with other important ERAS components such as -
Bodytracking with Microsoft Kinect
This is important because the aim of Telerobotics is to provide a way for astronauts to drive around the UGV on the Martian terrain. The step estimation data from the ERAS Bodytracking server is used to drive around the UGV in real-time. It is implemented in
telerobotics-bodytracking.py.EUROPA Scheduler and Planner
The scheduler is intended to be an astronaut’s mission field guide. The rover is also a part of the crew and needs to plan its trajectory around the Martian terrain for scientific experiments. This requires Telerobotics to interface with the existing ERAS Planner and navigate the Robot safely to the desired destination. The implementation is provided in
europa-navigation.py
The functional requirement of ERAS is control-command-communicate. Telerobotics realizes this in all aspects.
Diagnostics server¶
It is important for Mission Control to realize the real-time conditions of the Husky Robot. It is also necessary to use the Robot’s diagnostic information for various tasks such as resource planning and path optimization. To facilitate this, the Robot Diagnostic server is created. Implementations are provided in robot-diagnostics-server.py and robot-info-collector.py.
Fallback Interfaces¶
Telerobotics is a network-intensive high-performance application. In the unintended case of breakdown of the Bodytracking server or the Tango-Controls system, it is necessary to keep controlling the Husky rover. Keyboard Teleoperation is suggested to help in this case.
An implementation is provided for right-handed astronauts in the file teleoperation-keyboard.py.
Streaming¶
Streaming is a necessary requirement for ERAS. The video feed from the stereoscopic camera mounted on the Husky rover is streamed in real-time to Mission Control which is then processed and sent to the astronaut who can decide the future actions of the rover.
The implementation is provided in the eras/servers/telerobotics/streams/ directory.